Knowledge Base
DigiCert® Trust Lifecycle Manager | Windows Hello for Business integration guide
Introduction
This chapter includes the following topics:
- About Windows Hello for Business
- How DigiCert Contributes in Windows Hello for Business
About Windows Hello for Business
Windows Hello® for Business, a feature by Microsoft® starting from Windows 10, introduced password replacement with strong two-factor authentication, consisting of a new type of user credential bound to a device and accessed using a biometric or PIN. DigiCert now has an offering to issue certificates from the DigiCert® Trust Lifecycle Manager hosted Certificate Authorities for this new user credential.
For a detailed overview of Windows Hello for Business, please refer to the official Microsoft documentation: Windows Hello for Business Overview.
How DigiCert Contributes in Windows Hello for Business
Windows Hello for Business depends on multiple technology stacks, but Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) is one of its many foundations. DigiCert® Trust Lifecycle Manager can provide all certificates which are required to enable Windows Hello for Business through our Certificate Authority, and automatically provision them via our Autoenrollment Server.
The following table shows the type of certificates required by Windows Hello for Business.
Certificate Type
Required By
Description
Domain Controller
Domain Controllers (DC)
Certificate to install in DC to assure that the server is trusted.
Windows Hello for Business Authentication
End users
Certificate used by end users to authenticate to Active Directory or Azure. This is used in the background after successful PIN or biometrics authentication.
Enrollment Agent
Active Directory Federation Services (AD FS)
Certificate used by AD FS to sign Windows Hello for Business Authentication certificate request sent from end users.
SSL/TLS Server
Active Directory Federation Services
Certificate to install in AD FS to assure that the service is trusted.
Installation for this type of certificate is not covered in this document, but you can issue private server certificate using Generic Server template. Refer to DigiCert® Trust Lifecycle Manager | Autoenrollment Server deployment guide for details. For public server certificate, please contact our sales representative.
The above table only covers certificates required by Hybrid Azure AD joined Certificate Trust Deployment model which DigiCert supports currently. See below, “Supported Deployment Model and Trust Type” for more details.
The below sections describe how they are used and issued in more detail.
Windows Hello for Business Authentication Process
Windows Hello for Business enables users to use PIN or biometrics to authenticate, but PIN or biometrics are only used to access the private key stored in the device. They act as a key to open a box which stores the master key. The authentication with Active Directory and Azure solely relies on authentication requests signed by this private key.
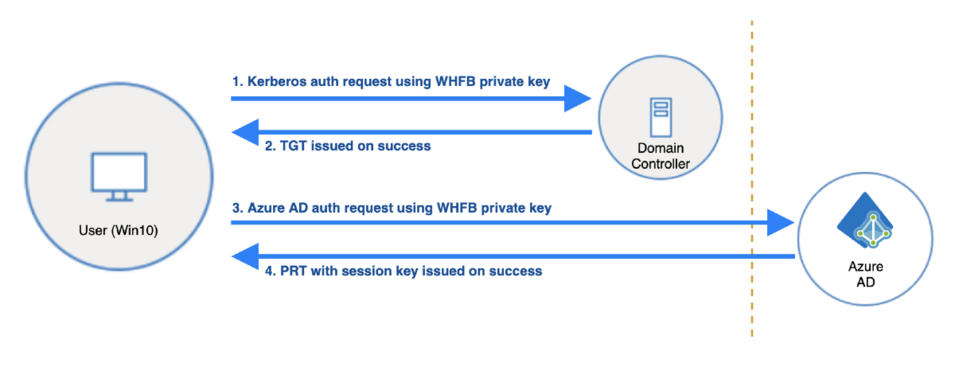
The above diagram shows the authentication process using Windows Hello for Business. After the user has retrieved the Ticket Granting Ticket (TGT) and Primary Refresh Token (PRT), he/she can access any on-premise service with Kerberos Authentication using TGT and any Azure service using PRT. For more information about PRT and TGT, check the following links.
Additionally, when the user authenticates with the Domain Controller, it is required that the server has the correct DC certificate. This is because the user also checks if the Domain Controller can be trusted.
For more details about the authentication sequence, check the following link.
Windows Hello for Business Certificate Issuance Process
The following diagram shows how the Windows Hello for Business Authentication certificate is issued to the end user using DigiCert Certificate Authority using Autoenrollment Server.
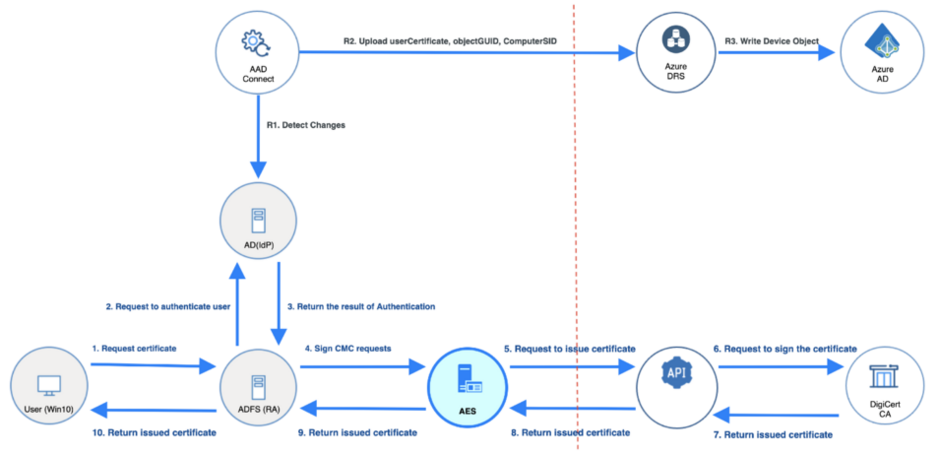
You can see from the diagram that the user requests the certificate through AD FS. AD FS authenticates the user and also signs the CSR (Certificate Signing Request) sent by the user. This is called “Enroll on Behalf of”, since AD FS enrolls for the certificate on behalf of the user. This process requires that AD FS has its own Enrollment Agent certificate, which is automatically issued to AD FS during this process if AD FS does not have an Enrollment Agent certificate.
The request is sent to Autoenrollment Server using CMC (Certificate Management over CMS), where Autoenrollment Server checks the signature of the request. If the signature is valid, Autoenrollment Server will call the DigiCert API to issue the certificate. The issued certificate will be returned to AD FS, and AD FS will return it to the user.
The issuance process explained in this section is also part of a process called “Provisioning“ in Windows Hello for Business terms, where initial certificate issuance occurs after the user has successfully authenticated to both Active Directory and Azure AD using credentials or MFA (Multi-Factor Authentication).
For more details about the certificate issuance sequence, check the following link.
Pre-requisites
This chapter includes the following topics:
- Supported Deployment Model and Trust Type
- Required Windows Hello for Business Setup
- Required Autoenrollment Server Setup
Supported Deployment Model and Trust Type
When enabling Windows Hello for Business for your organization, you will need to decide which deployment model and trust type suit your organization. Microsoft supports five different deployment models and trust type combinations:
- Cloud Only Deployment
- Hybrid Azure AD joined Certificate Trust Deployment
- Hybrid Azure AD joined Key Trust Deployment
- On-premises Certificate Trust Deployment
- On-premises Key Trust Deployment
Check the official Microsoft documents, Planning a Windows Hello for Business Deployment and Windows Hello for Business Deployment Prerequisite Overview for full details about which model you should and can use.
You do not need to be concerned about Windows Server Certificate Authority stated in the Microsoft Prerequisite document, since it will be covered by DigiCert.
Currently, DigiCert supports the Hybrid Azure AD joined Certificate Trust Deployment model but is planning to support additional certificate-based trust models. DigiCert will not support any of the two “Key Trust Deployment models”.
Required Windows Hello for Business Setup
The following shows the steps required to set up a Windows Hello for Business solution for Hybrid Azure AD joined Certificate Trust Deployment. They are steps outlined in the official Microsoft deployment guides. The links for each step will take you to the official Microsoft documents.
- Hybrid Certificate Trust Deployment Overview
- Prerequisites
- New Installation Baseline - skip “Public Key Infrastructure” section
- Device Registration
- Configure Windows Hello for Business settings
- Active Directory
- Public Key Infrastructure - replaced by this document
- Active Directory Federation Services - “Configure the Registration Authority” section replaced by this document
- Group Policy
- Active Directory
- Sign-in and Provision
You will need to complete all steps to 5-a. “Active Directory”, but in 3. “New Installation Baseline“, skip “Public Key Infrastructure” section. Also you can skip 5-b. “Public Key Infrastructure” and 5-c. “Active Directory Federation Services“, and finish 5-d. “Group Policy” first. This document replaces those sections, substituting Windows Server Certificate Authority with a DigiCert Certificate Authority.
When all the steps covered in this document are completed, you can move on to 6. “Sign-in and Provision”. If all the configurations are properly in place, provisioning should happen when the user logs on to their Windows machine.
Required Autoenrollment Server Setup
To enable Windows Hello for Business certificates to be issued from a DigiCert Certificate Authority, the DigiCert Autoenrollment Server is required to be installed and configured in your enterprise Windows domain. Follow the directions in DigiCert® Trust Lifecycle Manager | Autoenrollment Server deployment guide to install and configure.
All steps from the document need to be completed, and it is recommended to first check if certificates can be issued using a Non-Windows Hello for Business Certificate Profile. The issuance process for Windows Hello for Business is complicated, and it will be easier to troubleshoot by ensuring that your Autoenrollment Server can issue certificates properly before configuring for the Windows Hello for Business solution.
DigiCert has qualified Windows Hello for Business solution with DigiCert Autoenrollment Server and ADFS running on Windows Server 2022. Previous versions of Windows Server may work, but these have neither been formally qualified nor claimed by DigiCert. |
Setting Up Windows Hello for Business with Autoenrollment Server
This chapter includes the following topics:
- Creating Certificate Profiles
- Downloading and Importing Autoenrollment Configuration File
- Assigning Group/User Access for Each Template
- Issuing Domain Controller Certificates
- Setting Up Active Directory Federation Services
- Adding UPN to Service Account
- Provisioning
You will need to create three different certificate profiles from each certificate template described below to enable Windows Hello for Business for your organization.
Certificate Template Name
Description
Domain Controller
For Microsoft® Domain Controller certificates. Enables authentication of computers or other devices to your Active Directory domains, including users making use of Windows Hello for Business credentials.
Microsoft® Enrollment Agent
Enables organizations to issue Microsoft® Enrollment Agent certificates which allows for certificate enrollments on behalf of another entity in your Active Directory domains.
Windows Hello for Business Authentication
Enables organizations to issue Windows Hello for Business certificates to users in your Active Directory domains.
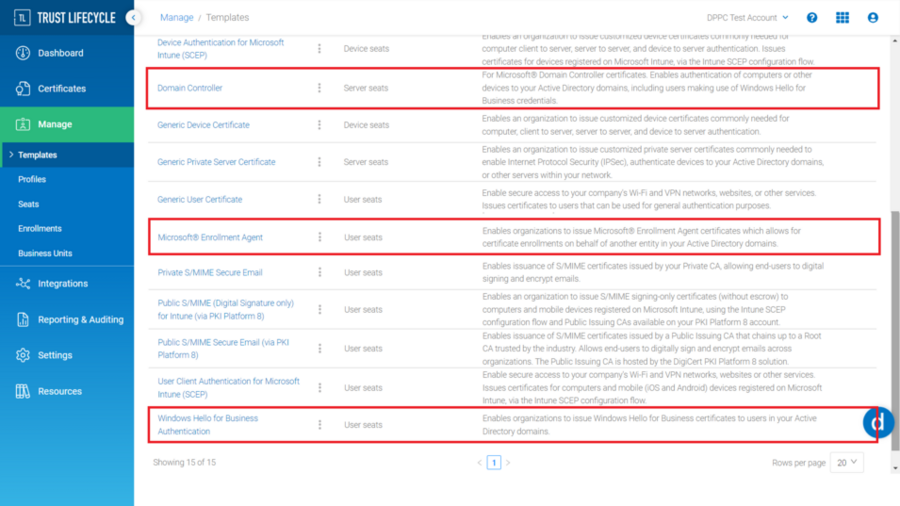
Please refer to the DigiCert® Trust Lifecycle Manager | Autoenrollment Server deployment guide, section “Creating Autoenrollment Certificate Profile”, which will guide you through how to create certificate profiles for Autoenrollment Server. When selecting a certificate template, ensure that you are selecting from one of the three templates described above.
After you create the profiles, make sure that you note the Profile GUID for the two profiles created from the following templates.
- Microsoft® Enrollment Agent
- Windows Hello for Business Authentication
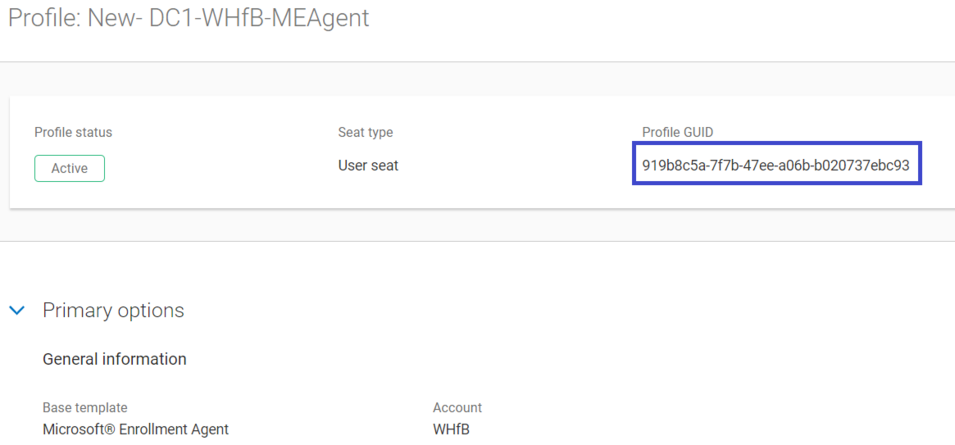
This information will be required later in section “Setting Up Active Directory Federation Services”.
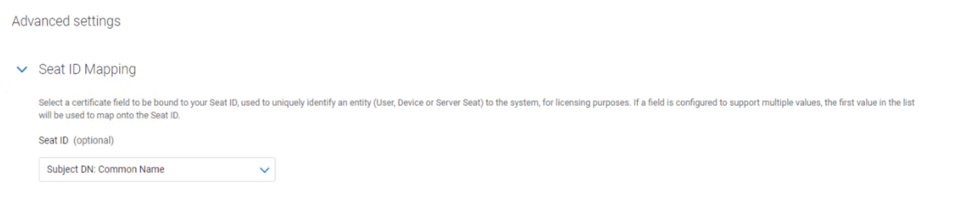
NOTE: Microsoft® Enrollment Agent template Seat ID will be mapped to ‘cn’ (Common Name) by default. This should not be changed to mail when the AD FS is run by Service Accounts, since Service Accounts do not have an email address.
Downloading and Importing Autoenrollment Configuration File
After you have successfully created the required three certificate profiles, you will need to download and import the Autoenrollment configuration file.
To do so, refer to the DigiCert® Trust Lifecycle Manager | Autoenrollment Server deployment guide section “Import the Autoenrollment Configuration File”.
Assigning Group/User Access for Each Template
After you have imported the Autoenrollment configuration file into the Autoenrollment Server, you will need to assign access permissions to the imported templates. The required permission for each template is described below. Refer to the DigiCert® Trust Lifecycle Manager | Autoenrollment Server deployment guide section “About the Preparation of Certificate Templates” and “About the Assignment of Group/User Access to Templates“ for more details on how to configure them.
Certificate Template Name
Target Group or User
Required Access Permission
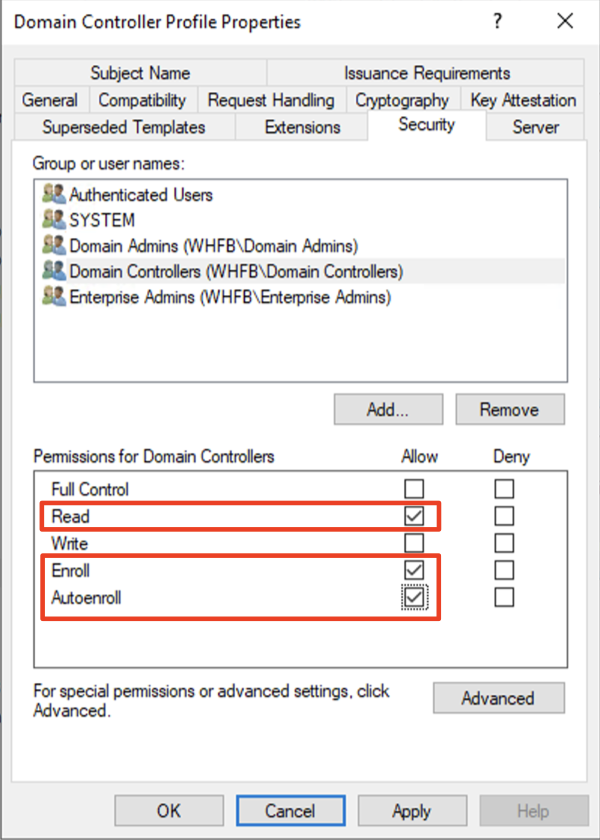
Domain Controller
Group which has all the Domain Controllers in your domain.
By default, Domain Controllers group should include all the domain controllers.
Check Read, Enroll, and Autoenroll.
Microsoft® Enrollment Agent
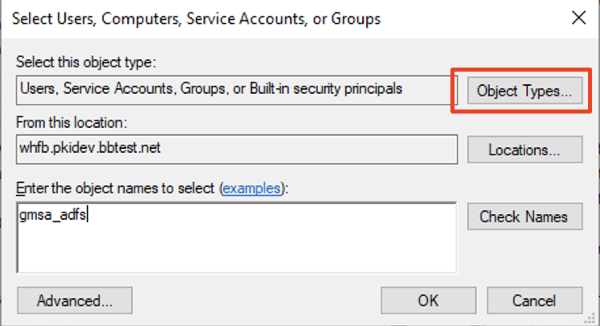
Group which includes the account user for AD FS, or specify the account directly.
If the account is a Service Account, the following operation is required to show the Service Account objects:
- After clicking Add click Object Types
- Check Service Accounts
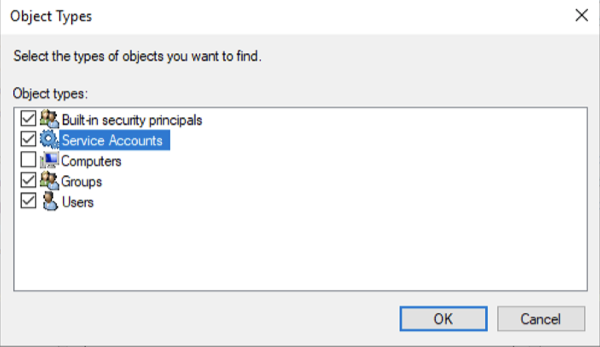
Check Read, and Enroll. Autoenroll is not required. Certificate from this template will be issued to AD FS account user automatically as part of Windows Hello for Business flow.
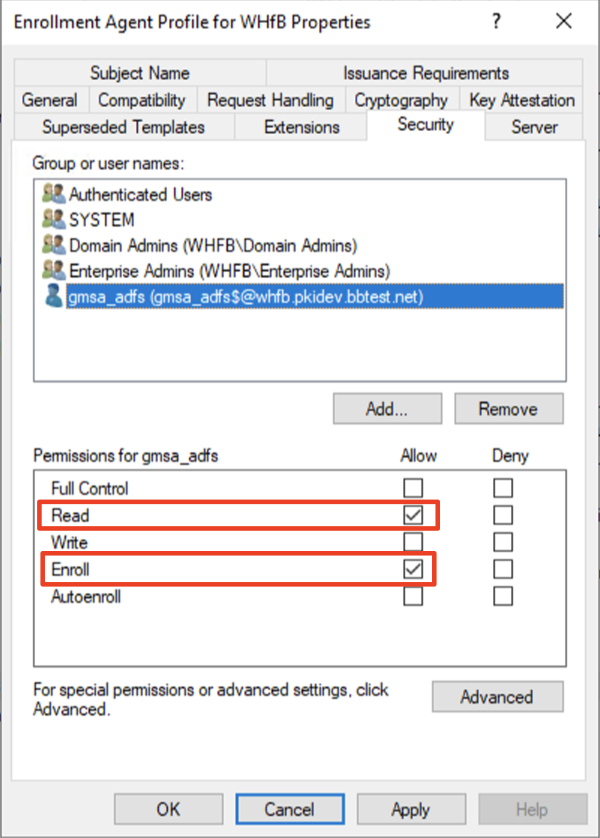
Windows Hello for Business Authentication
This should be Windows Hello for Business Users group that was created during 5-a. “Active Directory” from the official Microsoft documentation. The name does not have to exactly match, but needs to be group of users that you are trying to assign Windows Hello authentication to.
Check Read, Enroll, and Autoenroll.
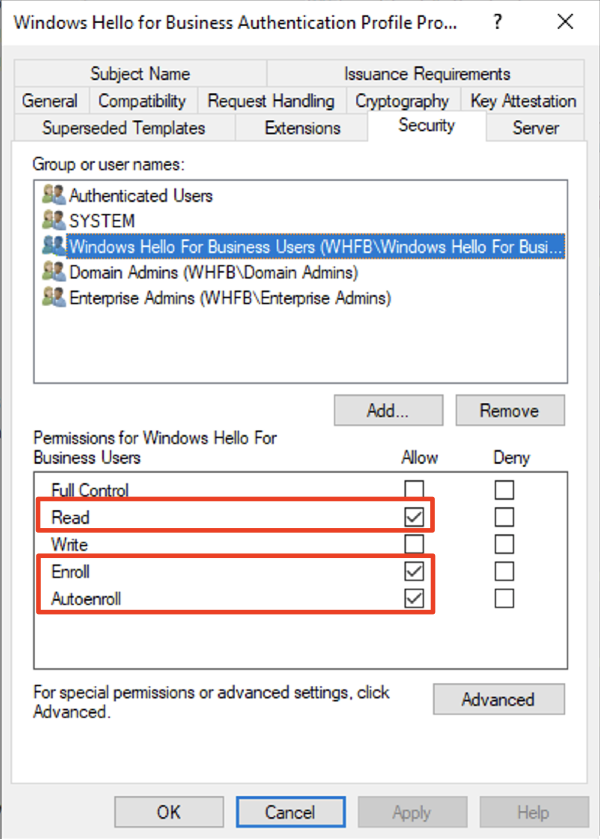
Issuing Domain Controller Certificates
After you have assigned access permissions to the Domain Controller template for the Domain Controllers, Domain Controller certificate will be issued automatically to the Domain Controllers. The timing depends on how the operating system handles them. To make sure that the certificate has been issued properly to the Domain Controllers, follow the instructions below.
To check for Domain Controller certificate:
- Sign in to the Domain Controller machine with Domain Admin equivalent credentials.
- Open Microsoft Management Console by typing [Windows] + [R], type mmc, and click OK.
- Add the Certificates Snap-in for the local computer.
- Open File menu, select Add/Remove Snap-in…
- Select Certificates and click Add
- Select Computer account and click Next
- Select Local computer and click Finish
- Click OK to close the Add or Remove Snap-ins window
- On the left pane, select Certificates (Local Computer) → Personal → Certificates and check if the Domain Controller certificate exists here.
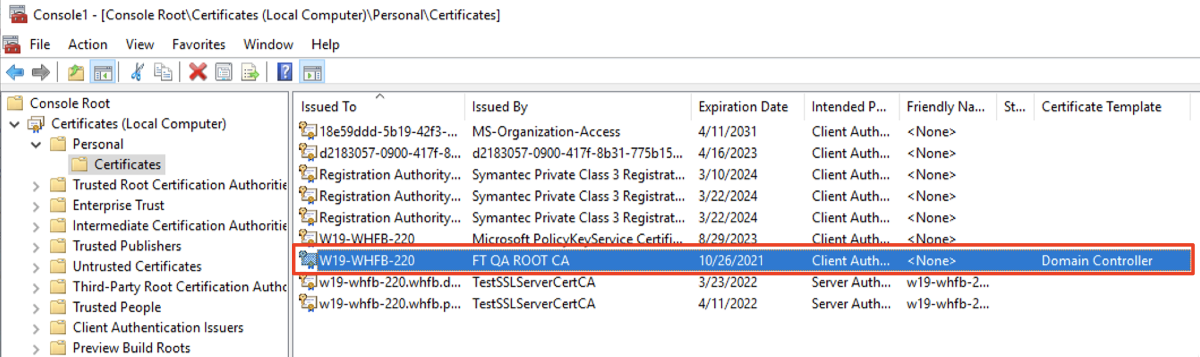
- Open File menu, select Add/Remove Snap-in…
Setting Up Active Directory Federation Services
After certificate templates are imported and access permission is set, you will need to configure the Registration Authority templates to use for Windows Hello for Business with AD FS. This section covers the first part of “Active Directory Federation Services“ from the Microsoft official documentation but provides little more information about what to specify for Windows Hello for Business Enrollment Agent and Windows Hello for Business Authentication template names when using DigiCert Autoenrollment Server.
To configure the Registration Authority:
- Sign in the AD FS server with Domain Admin equivalent credentials.
- Open a Windows PowerShell prompt.
- Enter the following command:
| Set-AdfsCertificateAuthority -EnrollmentAgent -EnrollmentAgentCertificateTemplate <Windows Hello for Business Enrollment Agent Profile GUID> -WindowsHelloCertificateTemplate <Windows Hello for Business Authentication Profile GUID> -WindowsHelloCertificateProxyEnabled $true |
For <Windows Hello for Business Enrollment Agent Profile GUID>, enter the Profile GUID for profile created using Microsoft® Enrollment Agent certificate template. For <Windows Hello for Business Authentication Profile GUID>, enter the Profile GUID for profile created using Windows Hello for Business Authentication certificate template. For example, it will look something like the following:
| Set-AdfsCertificateAuthority -EnrollmentAgent -EnrollmentAgentCertificateTemplate 919b8c5a-7f7b-47ee-a06b-b020737ebc93 -WindowsHelloCertificateTemplate c6dfa503-be5a-4c07-ad22-df14432f0666 -WindowsHelloCertificateProxyEnabled $true |
After the above configuration is completed, continue from “Group Memberships for the AD FS Service Account” in “Active Directory Federation Services“ from the Microsoft official documentation.
| Additionally, make sure that ‘ugs' scope is configured correctly as mentioned in the Note section of the document. This is extremely important since provisioning will not start without this ‘ugs’ scope properly configured. |
Adding User Principal Name to Service Account
This section will guide you on how to add User Principal Name (UPN) to Service Account. You will need to follow the direction here if your AD FS is configured to run using a Service Account. You can check whether AD FS is using Service Account by using the Services Tool (open Start Menu and type services). If Log On As for Active Directory Federation Services ends with '$' (dollar sign), this indicates that your AD FS is running using a Service Account.
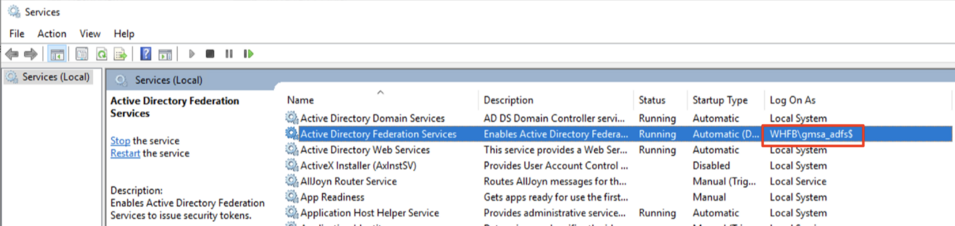
UPN is required to identify the end entity of the issued certificate, but since Service Account does not have UPN by default, it is required that this information is filled out before issuing Enrollment Agent certificate to the Service Account.
To add UPN to Service Account:
- Open Active Directory Users and Computers from Windows Administrative Tools.
- Click View and enable Advanced Features by selecting the option. This will enable editing the attribute of the Service Account.
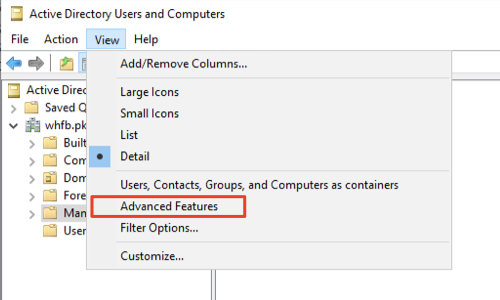
- In the tree window at the left, collapse the domain in which the Service Account exists, and select Managed Service Accounts. Right-click the Service Account configured for AD FS and select Properties.
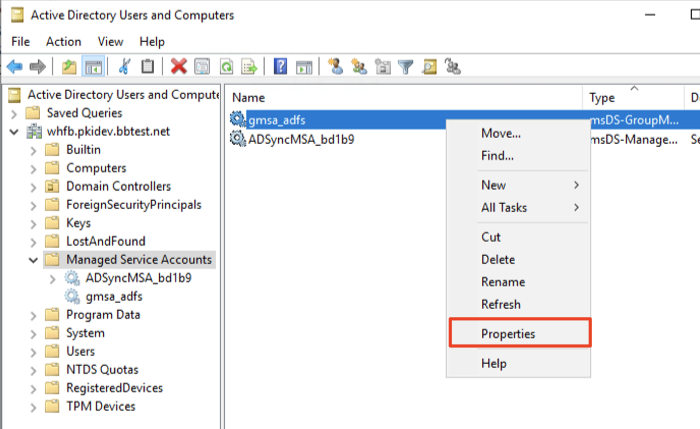
- In the Properties dialog, select the Attribute Editor tab, scroll down and select userPrincipalName. Click Edit.
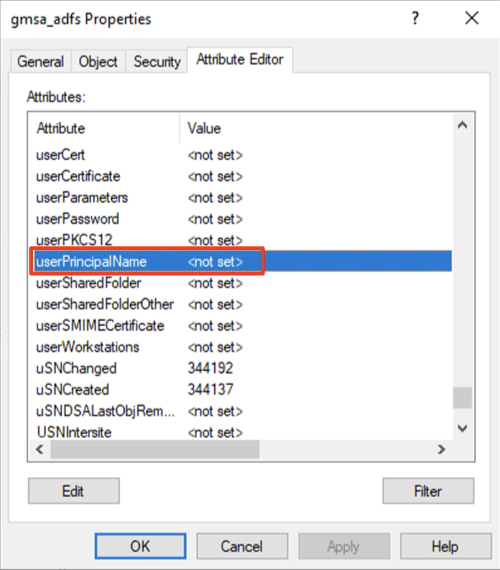
- In the String Attribute Editor dialog, enter userPrincipalName of the Service Account. UPN will need to be in the format, <cn of the Service Account>$@<domain name>. For this example, the cn (or the shown name) of the Service Account is “gmsa_adfs”, and domain is “whfb.pkidev.bbtest.net”. Resulting UPN for this example will be “gmsa_adfs$@whfb.pkidev.bbest.net”.
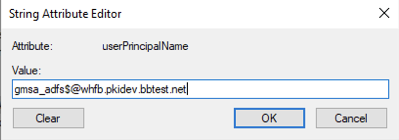
- Click “OK” twice to apply the change and close the dialogue.
After all configurations have been set and user logs on to their device, the user should be prompted to provision Windows Hello for Business. Refer to “Sign-in and Provision” from the Microsoft official documentation for details.
Windows Hello for Business Authentication Certificate Lifecycle
This chapter includes the following topics:
- Renewal
- Expiration
- Revocation
- Reset
Renewal of the certificate will occur in the background automatically when the certificate nears the expiration period. But for the certificate to renew, it requires the user to be logged in to the machine. If the user misses the renewal period for some reason, the certificate will reach expiration.
During Windows Hello for Business Authentication certificate renewal, only the certificate information is updated (such as validity notBefore and notAfter) and asymmetric keys are not regenerated.
When the automatic renewal does not occur during the renewal period for some reason, the certificate will expire. But users should be able to log on to their machine using the Windows Hello credential for the first time after certificate reaches the expiration. After successful login, the operating system will try to re-issue the certificate in the background. If the user logs out of the machine before this takes place, the user will not be able to login using their Windows Hello credential, with a screen like below.
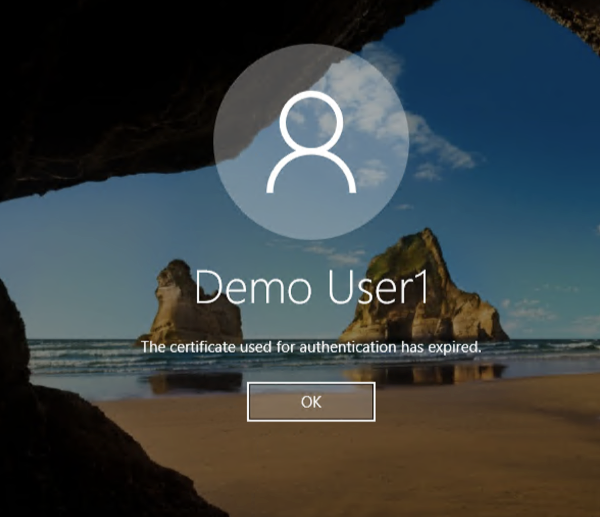
The user will need to login using Active Directory credential if this happens, but Windows Hello credential should be re-issued after some time automatically after successful login.
During re-issuance, only the certificate information is updated (such as validity notBefore and notAfter) and asymmetric keys are not regenerated.
When Windows Hello for Business Authentication certificate is revoked, the user will not be able to log in using their Windows Hello credential, with a screen like below.
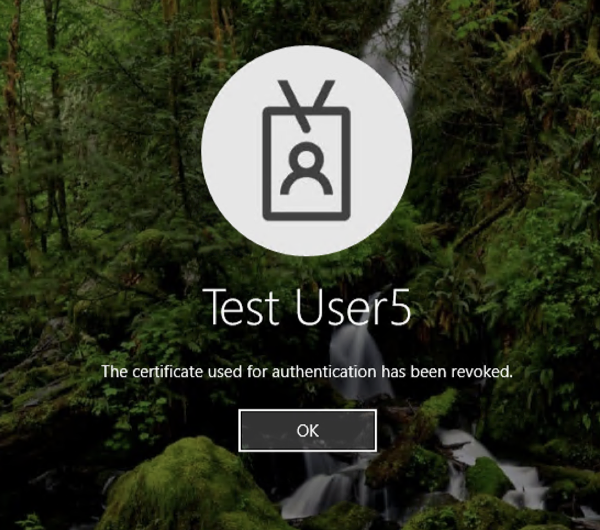
The timing in which OS identifies that the certificate is revoked depends on the update time of CRL or OCSP, so it may not be reflected immediately after the certificate is revoked.
The user will need to reset Windows Hello credential by such method as using “I forgot my PIN” in the login screen. See below “Reset” for more details.
When the user resets their Windows Hello credential such as using “I forgot my PIN” in the login screen, the user will be re-provisioned, and the certificate will be issued again. Asymmetric keys will be regenerated, and the new certificate will be issued. However, this will not revoke the previous user certificate on DigiCert® Trust Lifecycle Manager.
Known Issue
Active Directory Federation Service tries to issue a certificate for the Service Account from the Microsoft® Enrollment Agent profile every 12 hours to check the status of the Certificate Authority in spite of the certificate validity, configured on the Microsoft® Enrollment Agent profile. However, since the default value for Allow duplicate certificates is Disabled for the template, DigiCert Certificate Authority will reject the request, resulting in an error showing up under Windows Event Log (“Applications and Services Logs” → “AD FS” → “Admin”):
Error encountered while checking status of the AD FS enrollment certificate. Additional Data Exception details: Additional details: |
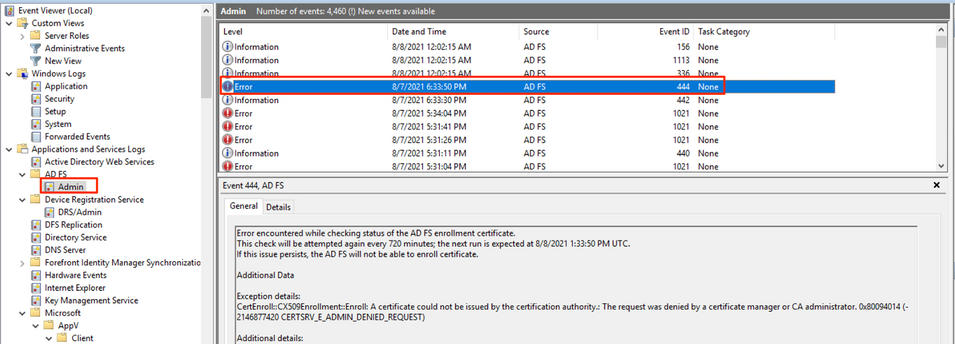
Screenshot of Windows Event Viewer Log
Also following CR_DISP_DENIED log entries will appear in AEServer logs for this request:
| 2022-06-29 11:24:03 INFO [4916] CBT_CertRequestD2::dispositionFromStatus()[BT_CertRequestD2.cpp:190]:INFO: disposition: 2 (CR_DISP_DENIED - Request denied) req state: RB_FAILED 2022-06-29 11:24:03 INFO [4916] CBT_CertRequestD2::Request2()[BT_CertRequestD2.cpp:980]:INFO: disposition after processNewTransaction: CR_DISP_DENIED - Request denied 2022-06-29 11:24:03 INFO [4916] CBT_CertRequestD2::Request2()[BT_CertRequestD2.cpp:981]:INFO: pdwRequestId -> 164 2022-06-29 11:24:03 INFO [4916] CBT_CertRequestD2::Request2()[BT_CertRequestD2.cpp:1022]:## Request2(): returning 0x0 |
DigiCert has already reported this issue to Microsoft, but we have come to a conclusion that this error entry will not impact the overall functionality of the Windows Hello for Business.
Even if you Enable the Allow duplicate certificates for Microsoft® Enrollment Agent profile, it will eventually result in the same error after 10 successful certificate issuance. This is due to DigiCert® Trust Lifecycle Manager only allowing 10 duplicate certificate issuance against the same Seat Id even if the profile allows it.