Knowledge Base
How Certificate Chains Work
Solution
What is a Certificate Chain?
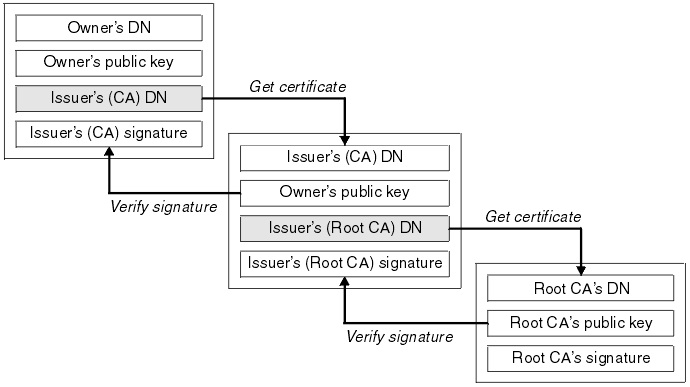
- A certificate chain is an ordered list of certificates, containing an SSL/TLS Certificate and Certificate Authority (CA) Certificates, that enables the receiver to verify that the sender and all CA's are trustworthy.
- The chain or path begins with the SSL/TLS certificate, and each certificate in the chain is signed by the entity identified by the next certificate in the chain.
What is an Intermediate Certificate?
- Any certificate that sits between the SSL/TLS Certificate and the Root Certificate is called a chain or Intermediate Certificate.
- The Intermediate Certificate is the signer/issuer of the SSL/TLS Certificate.
- The Root CA Certificate is the signer/issuer of the Intermediate Certificate.
- If the Intermediate Certificate is not installed on the server (where the SSL/TLS certificate is installed) it may prevent some browsers, mobile devices, applications, etc. from trusting the SSL/TLS certificate.
- In order to make the SSL/TLS certificate compatible with all clients, it is necessary that the Intermediate Certificate be installed.
What is the Root CA Certificate?
The chain terminates with a Root CA Certificate. The Root CA Certificate is always signed by the CA itself. The signatures of all certificates in the chain must be verified up to the Root CA Certificate.
Illustration of a certification path from the certificate owner to the Root CA, where the chain of trust begins: