Knowledge Base
What extensions and details are included in a SSL certificate?
Solution
The following fields are attributes that may be included in the SSL certificate details.
Note: with changing PKI standards, these attributes may change at any time without notice to comply with CA/B Forum requirements.
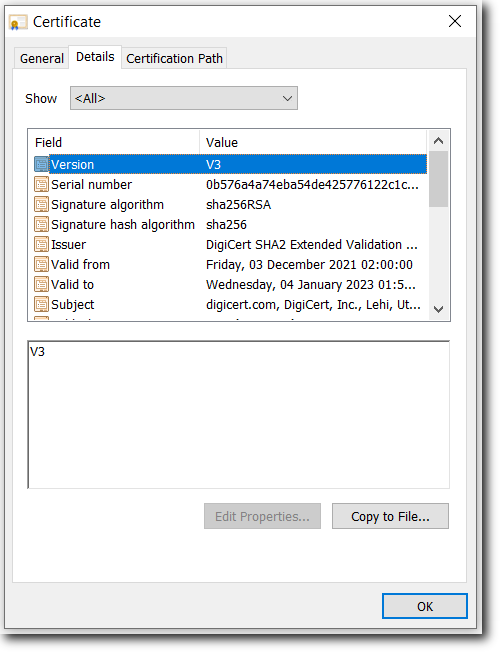
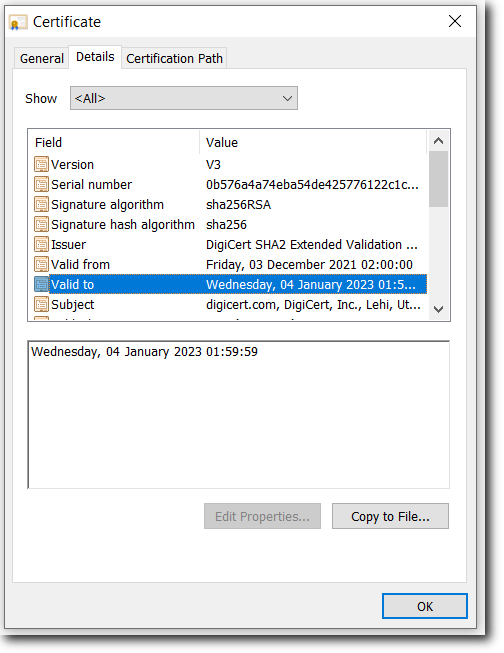
Version
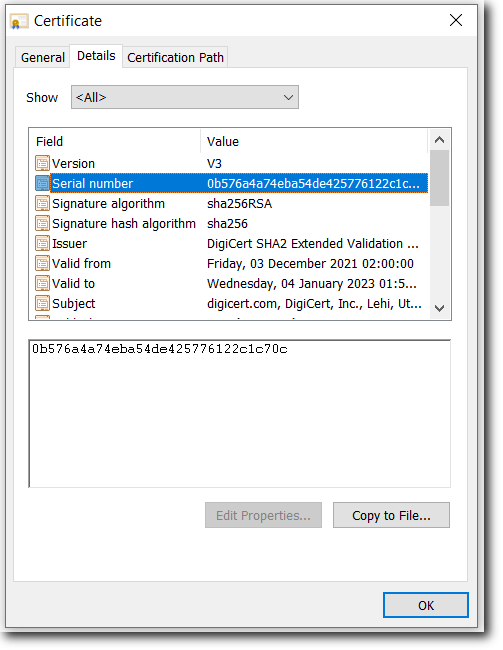
Serial Number
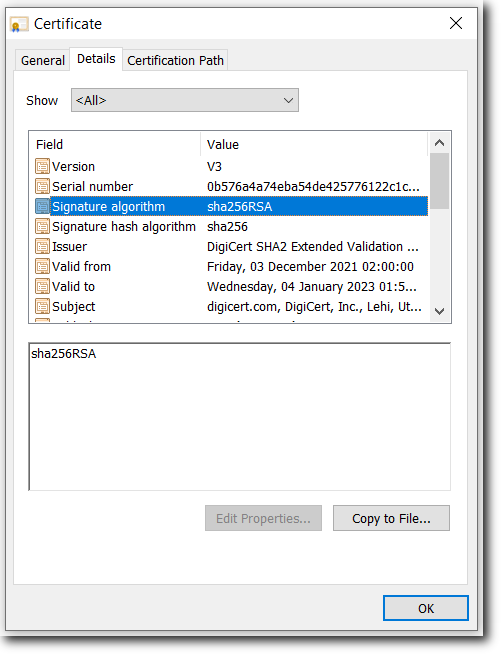
Signature Algorithm
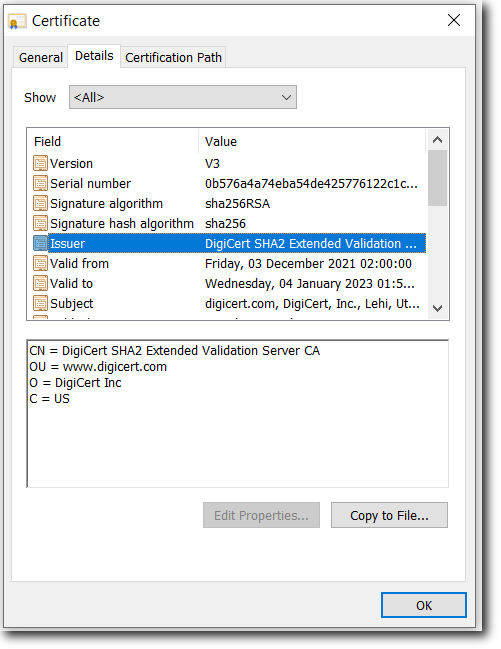
Issuer
Valid From and Valid To
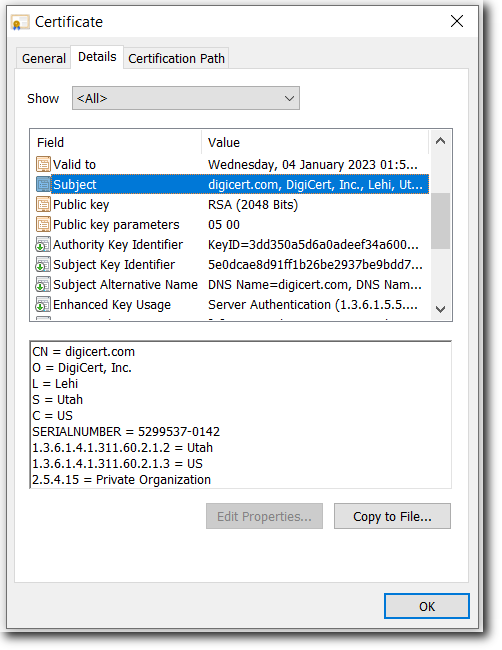
Subject
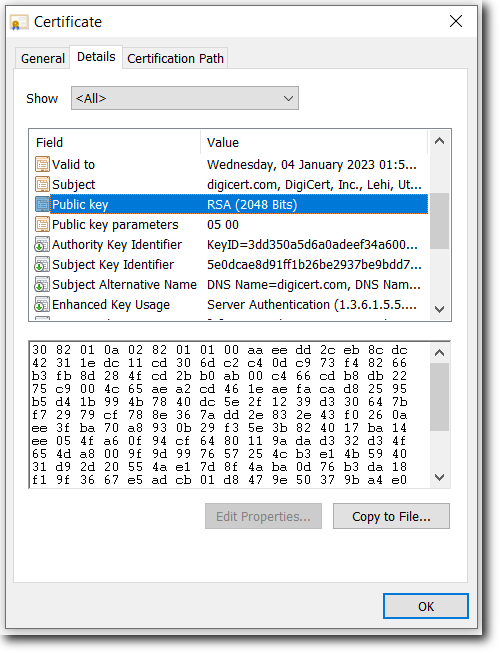
Public Key
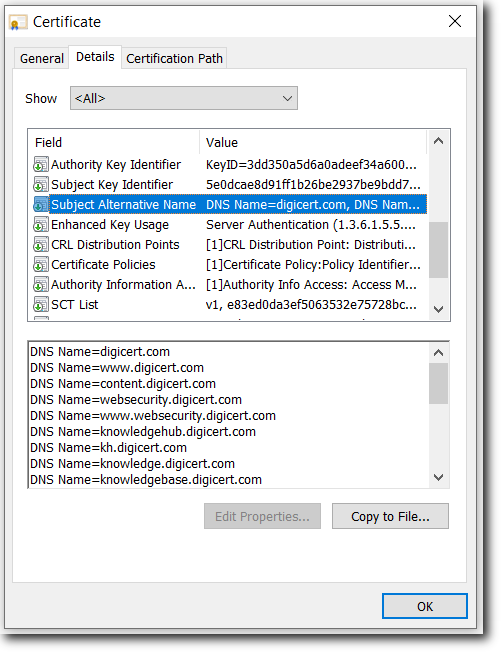
Subject Alternative Name (SAN)
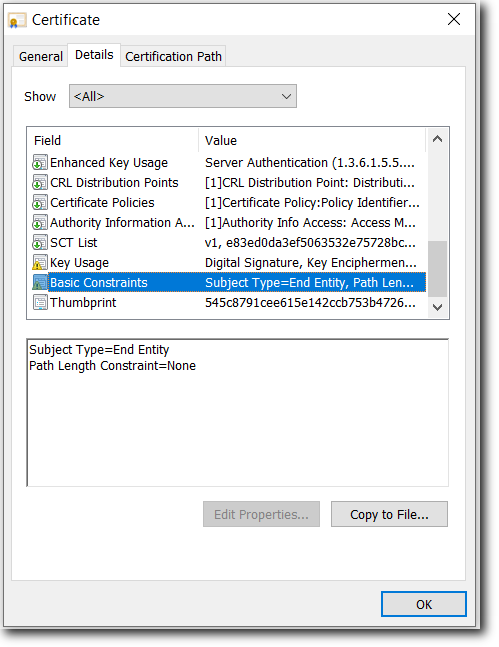
Basic Constraints
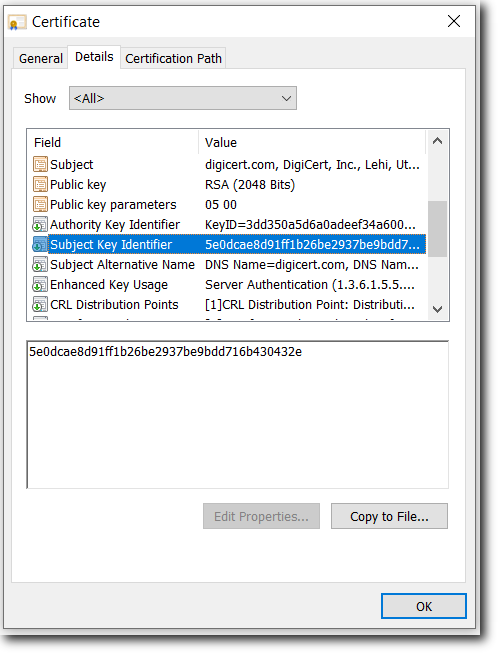
Subject Key Identifier (SKI)
Key Usage
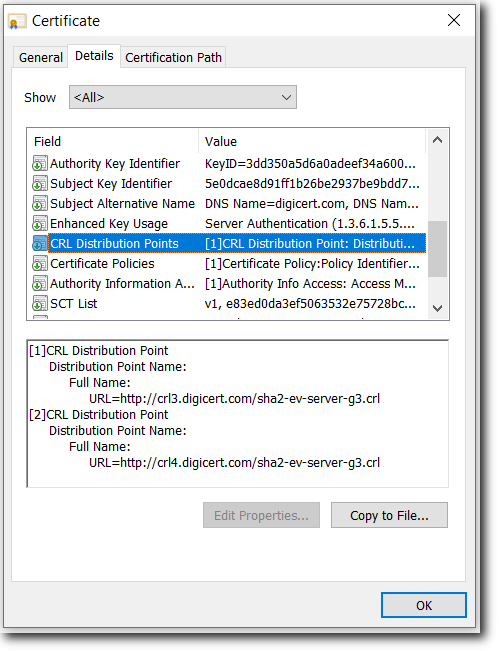
CRL Distribution Points
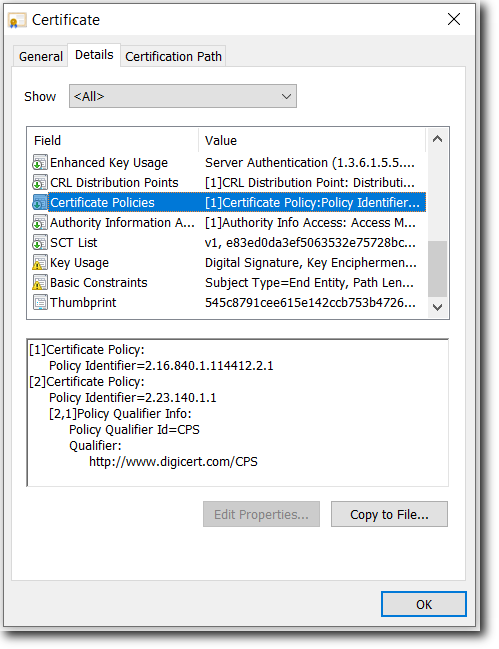
Certificate Policies
Extended Key Usage (EKU)
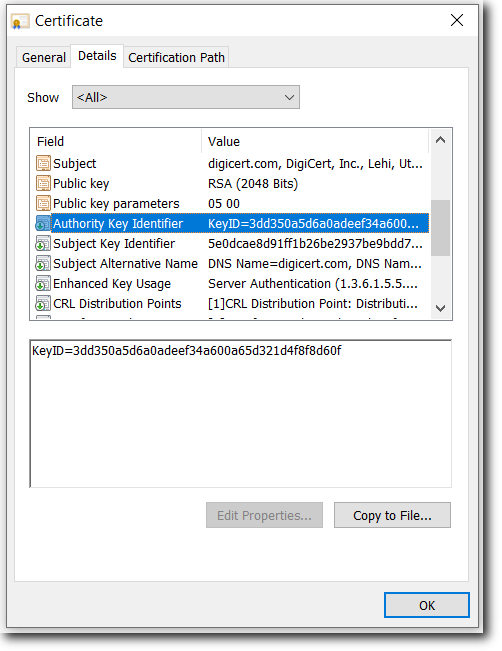
Authority Key Identifier (AKI)
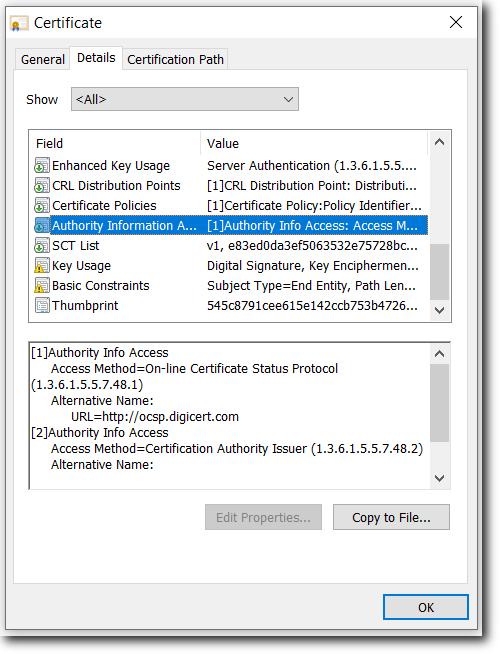
Authority Info Access
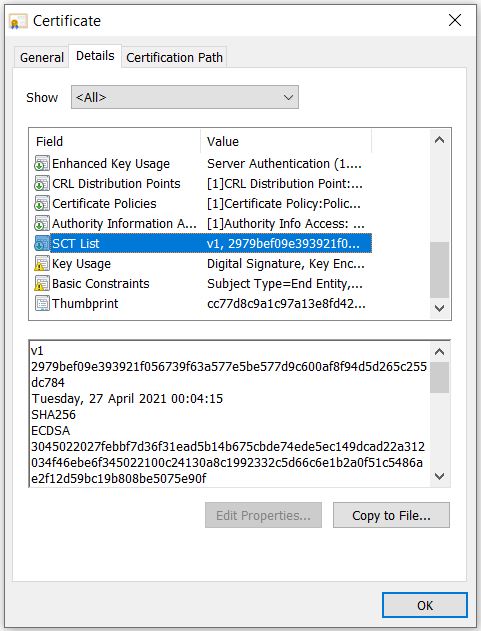
SCT List
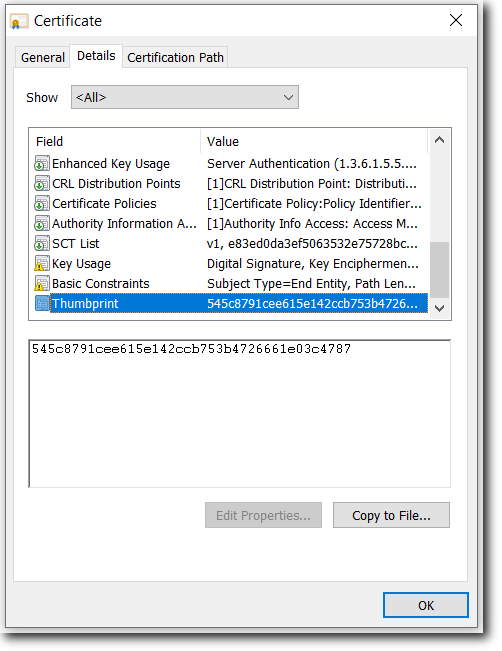
Thumbprint
This contains the Distinguished Name (DN) information for the certificate. The fields included in a typical SSL certificate are:
Common Name (CN)
Organization (O)
Locality or City (L)
State or Province (S)
Country Name (C)
For Extended Validation (EV) SSL certificates, these additional fields are also included:
Business Category
Serial Number (Business Registration Number)
Jurisdiction State
Jurisdiction Locality
The Key Usage extensions define what a particular certificate may be used for (assuming the application can parse this extension). The following extensions are included in an SSL certificate:
Digital Signature: (Taken from http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc3280.txt) The digitalSignature bit is asserted when the subject public key is used with a digital signature mechanism to support security services other than certificate signing (bit 5), or CRL signing (bit 6). Digital signature mechanisms are often used for entity authentication and data origin authentication with integrity.
Key Encipherment: (Taken from http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc3280.txt) The keyEncipherment bit is asserted when the subject public key is used for key transport. An example of Key Encipherment is the SSL handshake, where the two applications use asymmetric encryption to wrap around the exchange of a secret key that is ultimately used for the session.
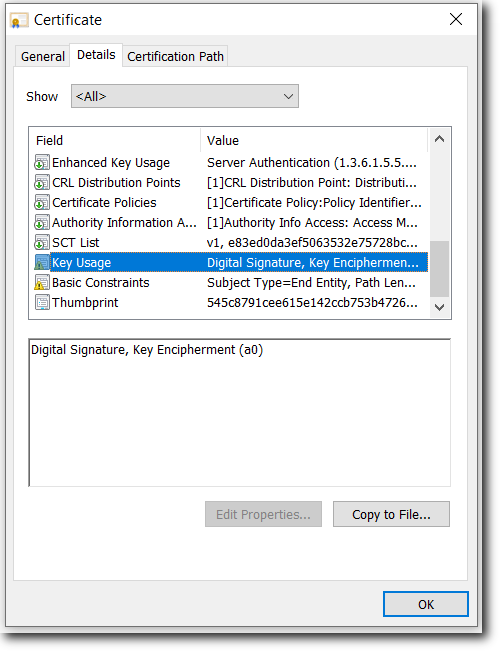
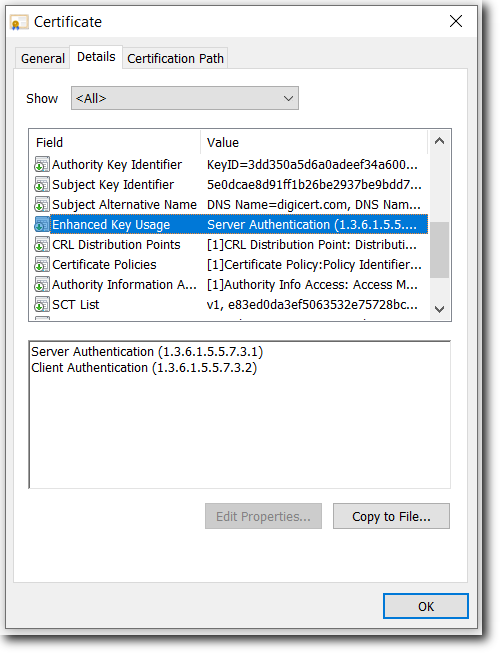
Also referred to as Enhanced Key Usage, this extension indicates one or more purposes for which the certified public key may be used, in addition to or in place of the basic purposes already indicated in the key usage extension.DigiCert SSL Certificates include the following extensions:
Server Authentication: (Taken from http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc3280.txt) TLS WWW server authentication. Key usage bits that may be consistent: digitalSignature, keyEncipherment or keyAgreement
Client Authentication: (Taken from http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc3280.txt) TLS WWW client authentication. Key usage bits that may be consistent: digitalSignature and/or keyAgreement
This extension provides the actual hash to ensure that the certificate has not been tampered with.
This information has been taken from RFC 3280: http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc3280.txt