Knowledge Base
Verify the Integrity of an SSL/TLS certificate and Private Key Pair
It's a three-part process to confirm the integrity of a key pair:
- Verify the integrity of a private key - that has not been tampered with.
- Verify the modulus of both private and public key match.
- Successfully perform encryption with the public key from the certificate and decryption with the private key.
- Confirm the integrity of the file which is signed with the private key.
Use OpenSSL to confirm the Private Key's Integrity
openssl rsa -in [key-file.key] -check -noout
Example of a private key that does not meet the integrity:
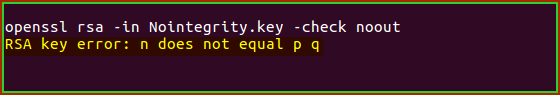
Some other errors that can be received from tampering/forging a key:
- RSA key error: p not prime
- RSA key error: n does not equal p q
- RSA key error: d e not congruent to 1
- RSA key error: dmp1 not congruent to d
- RSA key error: iqmp not inverse of q
If you received any of the above errors then your private key has been manipulated and may not work with your public key. Consider creating a new private key and requesting a replacement certificate.
Example of a private key that does not meet the integrity:
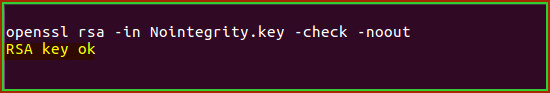
The above indicates a clean private key, proceed to the next step of comparing the modulus.
Confirm the Modulus Value Matching with Private Key and SSL/TLS certificate Key Pair
Note: The modulus of the private key and certificate must match exactly.
To view the certificate Modulus:
openssl x509 -noout -modulus -in [certificate-file.cer]

To view the private key Modulus:
openssl rsa -noout -modulus -in [key-file.key]

Perform Encryption with Public Key from certificate and Decryption with Private Key
- Get the public key from the certificate
openssl x509 -in [certificate-file.cer] -noout -pubkey > certificatefile.pub.cer
Example content of public key certificatefile.pub.cer file:
- Encrypt test.txt file content using the public key
Create a new file called test.txt file with the content "message test". Perform the following command to create an encrypted message to cipher.txt file.
openssl pkeyutl -encrypt -in test.txt -pubin -inkey certificatefile.pub.cer -out cipher.txt

Example output of cipher.txt:
- Decrypt from cipher.txt using the private key
Perform the following command to decrypt cipher.txt content.
openssl pkeyutl -decrypt -in cipher.txt -inkey [key-file.key]
Confirm that you are able to decrypt your cipher.txt file content to your terminal.
Make sure that the output from the terminal is matching the content on test.txt file.
If the content does not match, then the private key has been manipulated and may not work with your public key. Consider creating a new private key and requesting a replacement certificate.

Example output of successful decrypted message:

- Confirming the integrity of file which is signed with private key
Perform following command to sign test.sig and test.txt file with your private key
openssl dgst -sha256 -sign [key-file.key] -out test.sig test.txt
Verify the signed files with your public key that was extracted from step 1. Get public key from certificate.
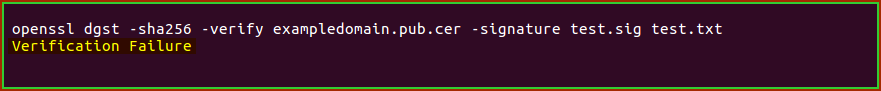
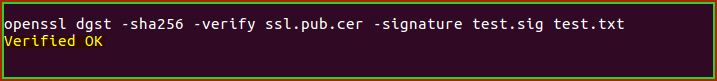
openssl dgst -sha256 -verify certificatefile.pub.cer -signature test.sig test.txt
Make sure that the output from terminal shows up like the example below.
An example that meets the integrity:
If you receive the below message, then your private key has been manipulated and may not work with your public key. Consider creating a new private key and requesting a replacement certificate.
An example that does not meet the integrity: