
Knowledge Base
Create a CNAME/ANAME Record Pool
Record pools were created to be used with load balancing techniques such as Round Robin, Failover, and our latency-based Traffic Steering solutions, and are used to manage the way traffic flows between multiple endpoints.
Implementing record pools into your DNS configuration improves speed and performance, and ensures none of your servers become overloaded.
Common Use Cases for CNAME and ANAME Record Pools
If you want to distribute traffic across multiple servers using a regular or weighted Round Robin configuration, you can add your hostnames or fully qualified domain names (FQDNs) to a pool and apply them to the same record, rather than creating a separate record for each host.
You can also create a failover record pool. This technique works similarly to
Round Robin except that with a failover pool, your traffic will only be sent to healthy resources in the pool. For instance, if you have a CNAME or ANAME record pointed to three different hostnames or FQDNs, and one of the hostnames in your pool is down, the downed hostname will not be returned.
To learn more about load balancing, and use cases, and to view video tutorials visit our DNS Load Balancing page.
Prerequisites
A domain has already been added to your Contellix account
You understand the basics of load balancing
Records have been created or imported for your domain
Configure CNAME/ANAME Record Pools in Constellix
1. Click Managed DNS and Select Pool
Once logged into Constellix, select Managed DNS in the left-hand sidebar menu. This will display a drop-down list of DNS configuration options. Next, select ANAME/CNAME Pools from the drop-down menu.
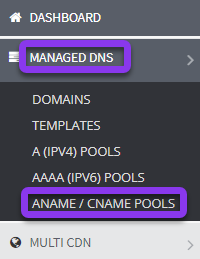
2. Click Add New Pool
Next, select the green + Add New Pool button on the right-hand side of the screen.
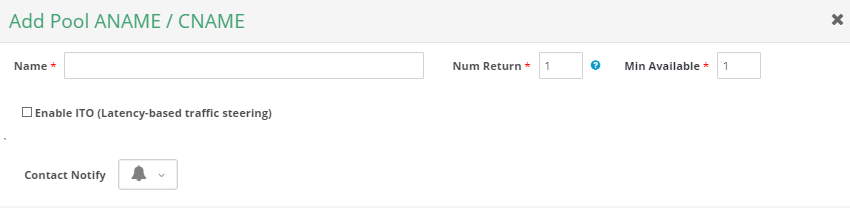
3. Enter Values
The Add Pool ANAME/CNAME pop-up window will display. Add the information for your pool by following the steps below:
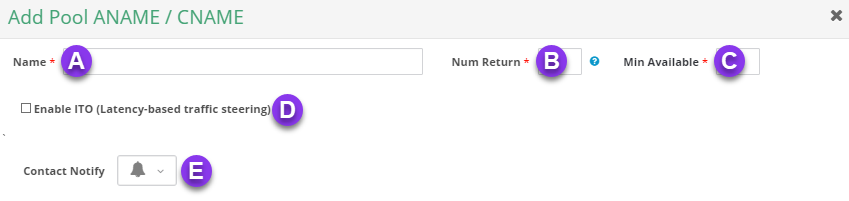
a) Name: Give your pool configuration an identifiable name.
b) Num Return: Enter the number of FQDNs you want to have returned in the pool.
c) Min Available: Enter the minimum number of FQDNs that must be available in the pool.
d) Enable ITO (Latency-based traffic steering): For more information on ITO, click here.
e) Contact Notify: This option allows you to select a contact list to send notifications to. For help setting up a contact list, go here.
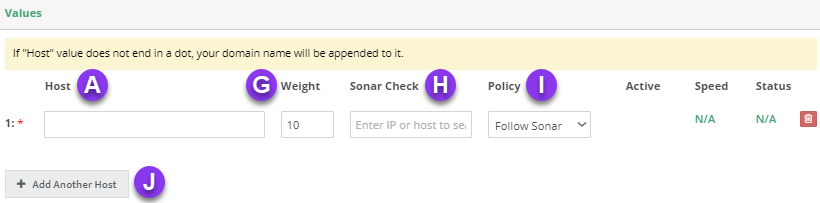
f) Host: The FQDN of the host you want to point to.
g) Weight: You can distribute weight equally between FQDNs in a pool, or choose a different weight for each host, depending on how you want to optimize your traffic. A higher weight will send more traffic to that IP. See our Weighted Round Robin tutorial to learn more.
h) Sonar Check: If you set Policy (see step I. below to "Follow Sonar" or "Off on Failure," click in the Sonar Check field and select the appropriate Sonar check in the drop-down menu (you can search through them by typing the associated FQDN in the text box).
Note: You can filter through the options by typing the associated FQDN in the text field.
If you do not choose "Follow Sonar" or "Off on Failure," skip this step.
i) Policy: There are four policies:
Follow Sonar - turns the record on or off depending on the status of your preconfigured Sonar Check.
Always On - ensures that the value is always active in the pool.
Always Off - ensures that the value is not returned. This allows you to keep the value "off," but kept in place for later use.
Off on Failure - similar to the Follow Sonar except once Sonar marks the check as "down," that specific record will no longer be returned, even after the resource becomes available again.
j) Add Another Host: You will need to click this option for each additional value you want to add to the record pool.
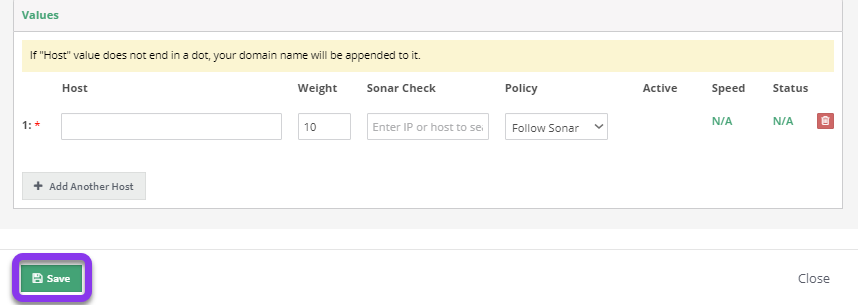
Once you have entered all the necessary values for your record pool, click the green Save button at the bottom left of the pop-up window to store the pool.
4. Apply Pool to Domain
Be sure to apply the pool(s) to your domain for your record pool configurations to take effect. To see how to apply a pool to your domain, click here.
Visit our website for more information on our services and features.

