
Knowledge Base
Create an ANAME Record
ANAME records were developed to function like a CNAME record, but with more flexibility. Unlike CNAMES, this record type allows you to point the root of your domain to a hostname or fully qualified domain name (FQDN ). This functionality is possible because ANAME records are actually a combination of CNAME and A records.
When an ANAME record is queried, the authoritative nameserver eventually resolves to the host or FQDN stored within the ANAME record. This means that even if the ANAME record itself can’t be resolved, the most recently cached IP address or host will be returned, which prevents unnecessary downtime. The way this works is by Constellix storing the value of the ANAME as an A record, while continuously monitoring for any changes in the record. If a change is made, the ANAME record will be updated automatically.
Common Use Cases for ANAME Records
As ANAME records perform similarly to CNAME records, they offer the ability to point the root of your domain to FQDNs or subdomains. There is also no lag in resolution times, as ANAME updates are done when queried, rather than upon TTL expiration. This is beneficial for mission-critical systems that require frequent updates, as well as systems that need the most accurate GeoDNS resolution. With ANAME records, it is also possible to have multiple authoritative, dynamically updated IP addresses for one domain in different regions, which is particularly useful for content delivery networks (CDNs).
ANAME records are compatible with all Constellix services, including Failover, Multi-CDN management, GeoDNS, Traffic Steering, and Load Balancing options such as Round Robin and Weighted Round Robin.
Prerequisites
- A domain is already added to your Constellix account
- You have all the necessary IP addresses or hostnames for your domain
Note: Visit our tutorials on creating records if you need help with record creation. If you need help adding a domain, we have a guide that walks you through the process.
How to Create an ANAME Record in Constellix
1. Log in to Constellix and Select Domain
Log into Constellix. Once in the dashboard, select your domain from the Recently Updated Domains list or search for the domain in the top-left search bar.
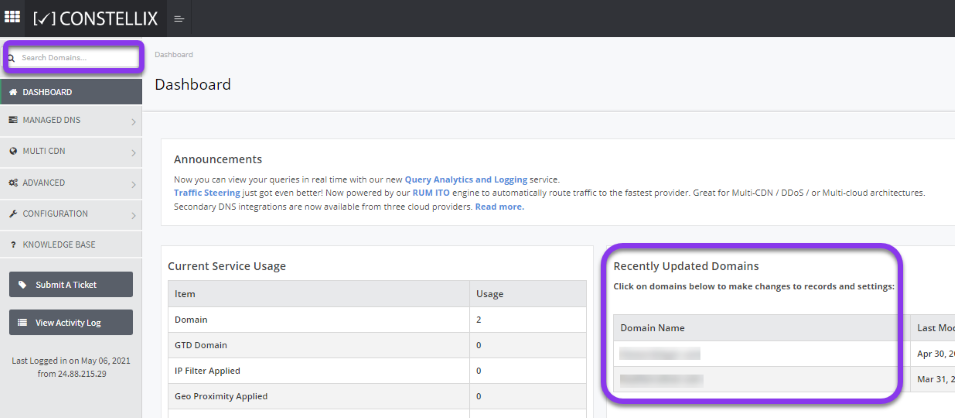
Note: Options available may vary depending on the current configurations set for your domain.
2. Expand ANAME Records
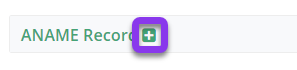
After selecting the domain that needs the ANAME record, you will be taken to the Records page. If you have not configured any ANAME records for this domain yet, click the green + icon beside ANAME record to expand options, otherwise skip to step 3.
3. Add ANAME Record
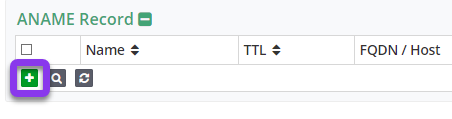
Scroll down to the ANAME section and click the green + icon to add an ANAME record.
4. Enter ANAME Record Values and Save
You should now see the Add ANAME Record pop-up window.
Fill out the following values:
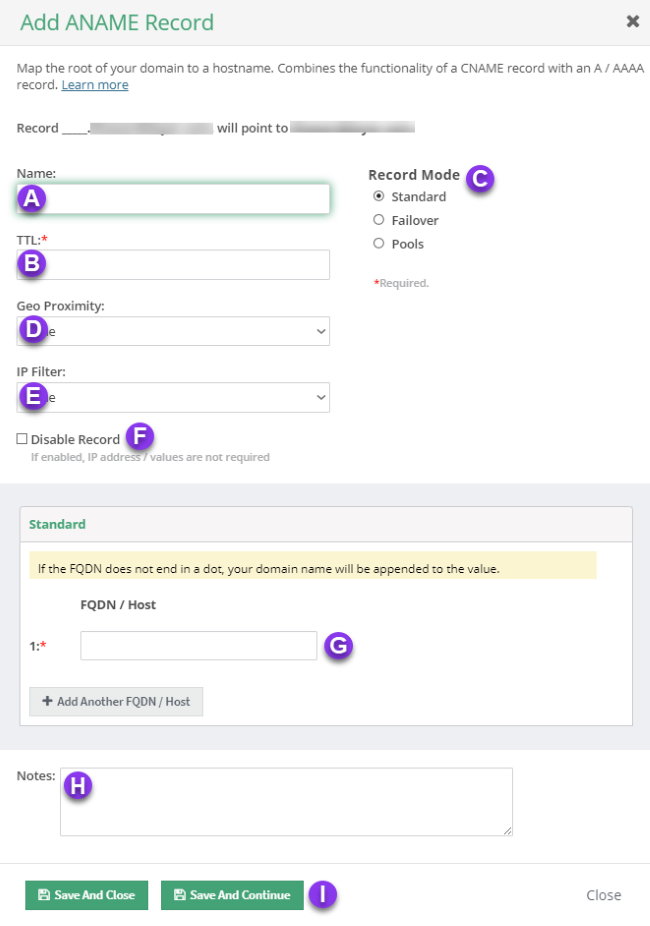
a) Name: Enter the FQDN/hostname for the record.
b) TTL: Time to live (measured in seconds) determines how long a record is cached in nameservers. Visit our What is TTL resource for more information and best practices for TTLs.
Note: For mission-critical records or those that require frequent updates, we recommend setting TTL values between 30 and 300 seconds. For failover configurations, 30 seconds is ideal for preventing end-user disruptions.
c) Record Mode: This mode lets you configure Failover, Record Pools, or Round Robin with Failover.
Visit our Records Mode page for more details.
d) Geo Proximity: Enable Geo Proximity rules that allow you to optimize web traffic by specifying the locations of IP addresses for your DNS ANAME records.
e) IP Filter: This option allows you to configure an IP Filter for an ANAME record.
f) Disable Record: With this feature, you are able to remove records from our nameservers without removing the record configuration in the Constellix DNS control panel.
See our Disabling a Record tutorial for more information.
g) Host: Enter the fully qualified domain name you want the ANAME record to point to.
h) Notes: The note section lets you add important details and keywords so you can easily search for specific records later (optional, but recommended).
i) Save: If you need to add an additional ANAME record, tap the green Save and Continue button, otherwise, click on Save and Close.
Note: In order for your ANAME record to take effect, you must review and apply changes.
Visit our website for more information on our services and features.

